
Buy Direct
from the Manufacturer
Sell our Products
Become a Distributor
Discounts
on volume purchases
Visit Us
at our Miami office
from the Manufacturer
Become a Distributor
on volume purchases
at our Miami office
A generator for home backup power comes in two main types: portable generators (starting around $450) and standby generators ($2,000-$7,000+). Portables require manual setup and refueling, while standby units start automatically during outages. The right choice depends on your budget, power needs, and how often you experience outages.
Quick Decision Guide:
Power outages are more than an inconvenience; they can be costly. As one homeowner noted, “If your sump pump stops and your basement floods, you’re looking at a costly repair.” For families with young children, elderly relatives, or anyone depending on medical equipment, a reliable backup power source is essential.
In storm-prone areas like South Florida, generators provide peace of mind during hurricane season. They keep refrigerators running, prevent food spoilage, maintain climate control, and ensure lights stay on. This guide covers everything you need to know about choosing, installing, and safely operating a home generator.
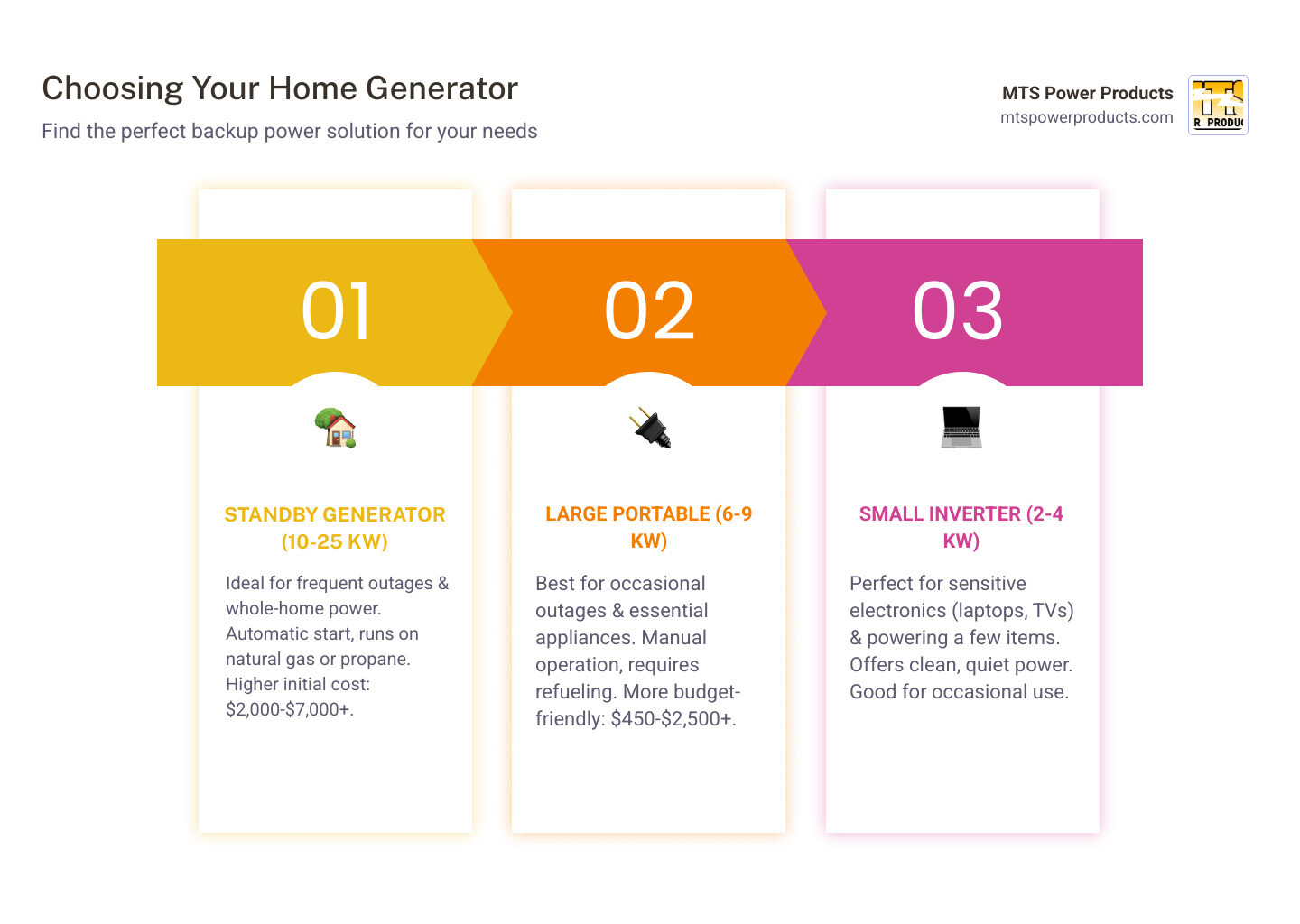
Generator for home vocab to learn:
When shopping for a generator for home use, you’ll find two main categories: portable and standby. Think of it as choosing between a powerful flashlight and a whole-house backup lighting system. Understanding the differences will save you time and money.
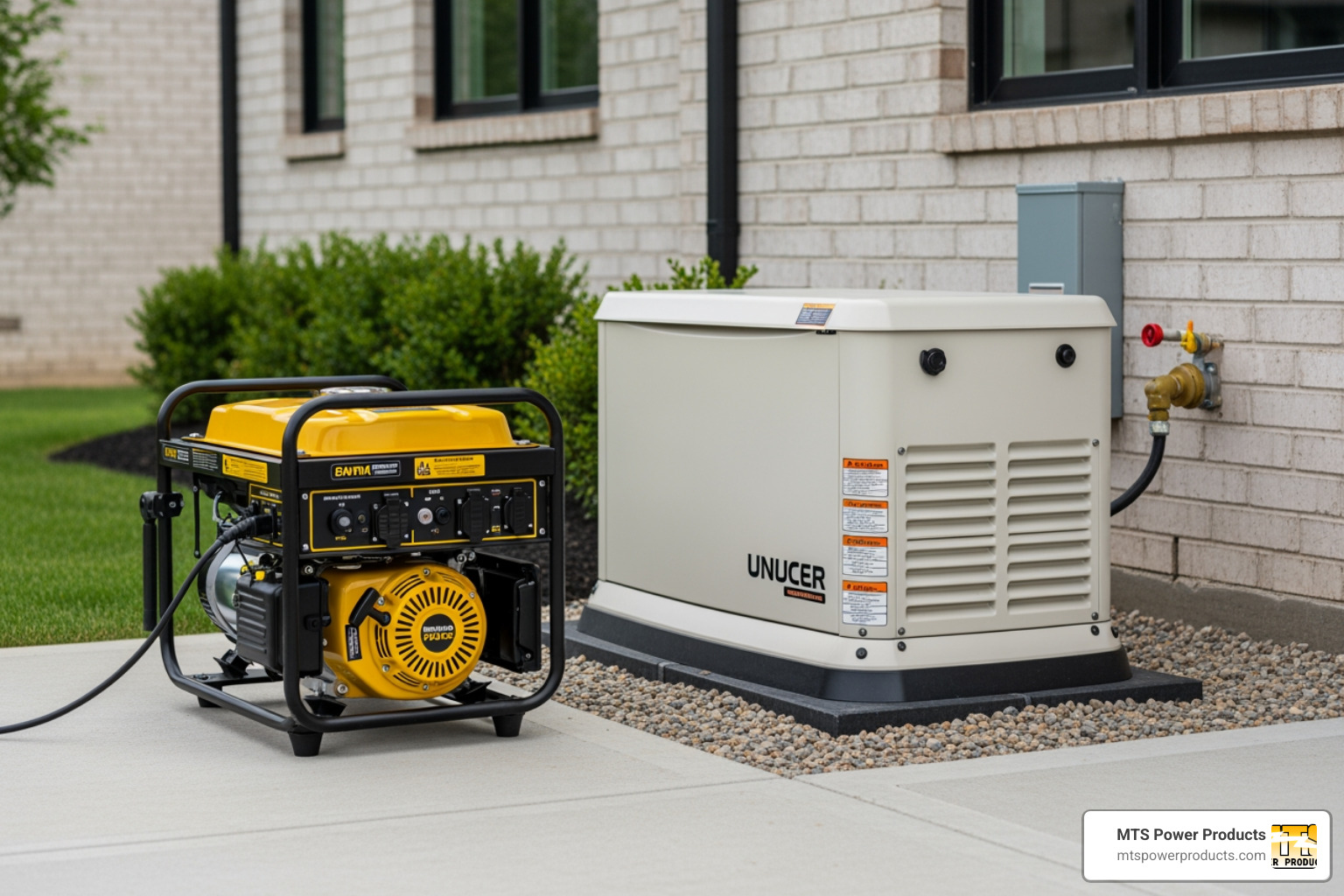

Portable generators are the Swiss Army knives of backup power. They’re designed to be moved, making them useful for home emergencies, camping, or remote jobsites. Their main draws are a lower upfront cost (starting around $450) and versatility. Small inverter models are lightweight (around 60 lbs), while larger units have wheels for easier movement.
However, portable generators have drawbacks. Manual operation means you must go outside to start it, connect extension cords, and manage the load. Refueling is also a constant task, as most run on gasoline and require safe storage and periodic refills. A critical safety rule: always turn off the generator and let it cool before refueling to prevent fires.
Other limitations include limited wattage compared to standby units and significant noise levels, though quieter inverter models are available. Most importantly, due to deadly carbon monoxide emissions, you must never operate a portable generator indoors, in a garage, or near windows.
Portable generators are ideal for occasional power outages, budget-conscious buyers, or those needing to power just the essentials like a refrigerator, lights, and chargers. For a quiet, reliable option, the Honda EU2200i Companion Portable Generator is known for its clean power output.
Standby generators are permanently installed outside your home, like an AC unit, and provide automated backup power. Their key feature is the automatic start. Within seconds of an outage, the generator detects the power loss, starts up, and restores electricity to your home, whether you’re there or not.
These units provide whole-home power, with capacities from 10 to 25 kilowatts or more, enough to run HVAC systems, appliances, and medical equipment simultaneously. The Generac Guardian 22-kW Standby Generator, for instance, can power a typical 2,500-square-foot home.
They run on natural gas or propane, connecting to your home’s existing fuel line. This eliminates the need for refueling; a natural gas connection provides a virtually unlimited runtime. A professionally installed standby generator also offers improved safety and can increase your home value.
The main downside is the higher initial cost. The unit itself costs $2,000 to $7,000+, and professional installation is required, adding several thousand dollars to the total. Once installed, it’s a permanent fixture that requires routine maintenance like oil changes and test runs.
Standby generators are best for homes in areas with frequent or prolonged outages, for those who prioritize convenience, or for households dependent on medical equipment. In South Florida, many homeowners consider them essential. For a convenient and reliable option, a natural gas powered generator is an excellent choice.
Choosing the right generator for home backup requires matching the machine to your needs. Let’s walk through the key decisions to find your perfect power solution.
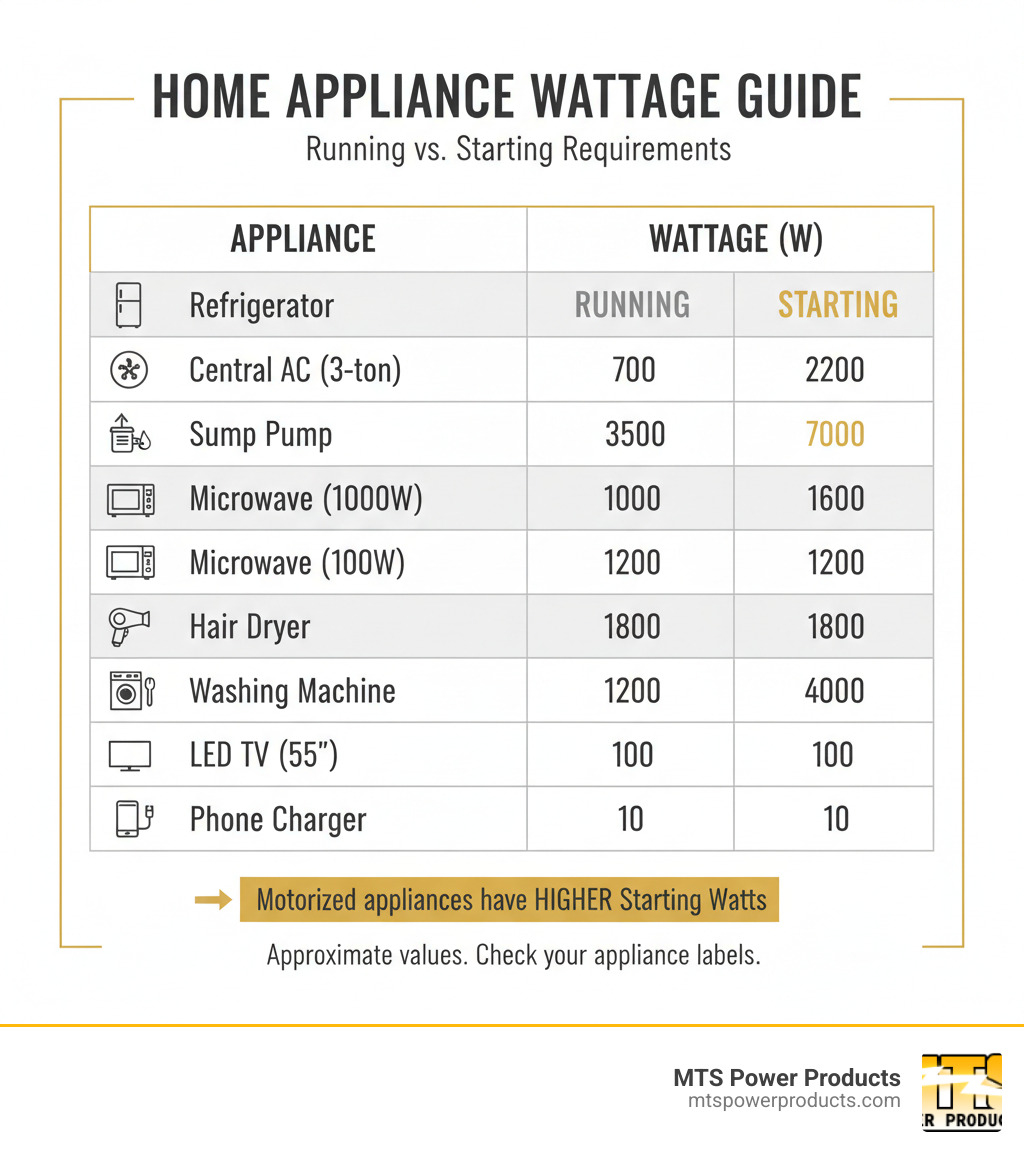
Buying a generator without knowing your power requirements is a gamble. Every appliance has two ratings: running watts (continuous power) and starting watts (the extra surge needed to turn on, especially for motors in refrigerators or AC units). This surge can be 2-3 times the running wattage.
To calculate your needs:
Pro Tip: Add a 10-20% buffer to your total. This prevents overloading the generator and extends its lifespan. As a guideline, 3,000-5,000 watts can handle essentials like a fridge and lights. For larger appliances or systems, you may need 10,000 watts or more.
For help, use an online calculator like this handy selector tool to walk you through the process.
Once you know your wattage, compare these features:
Your laptops, TVs, and smartphones need clean power to avoid damage. This is where inverter technology is crucial.
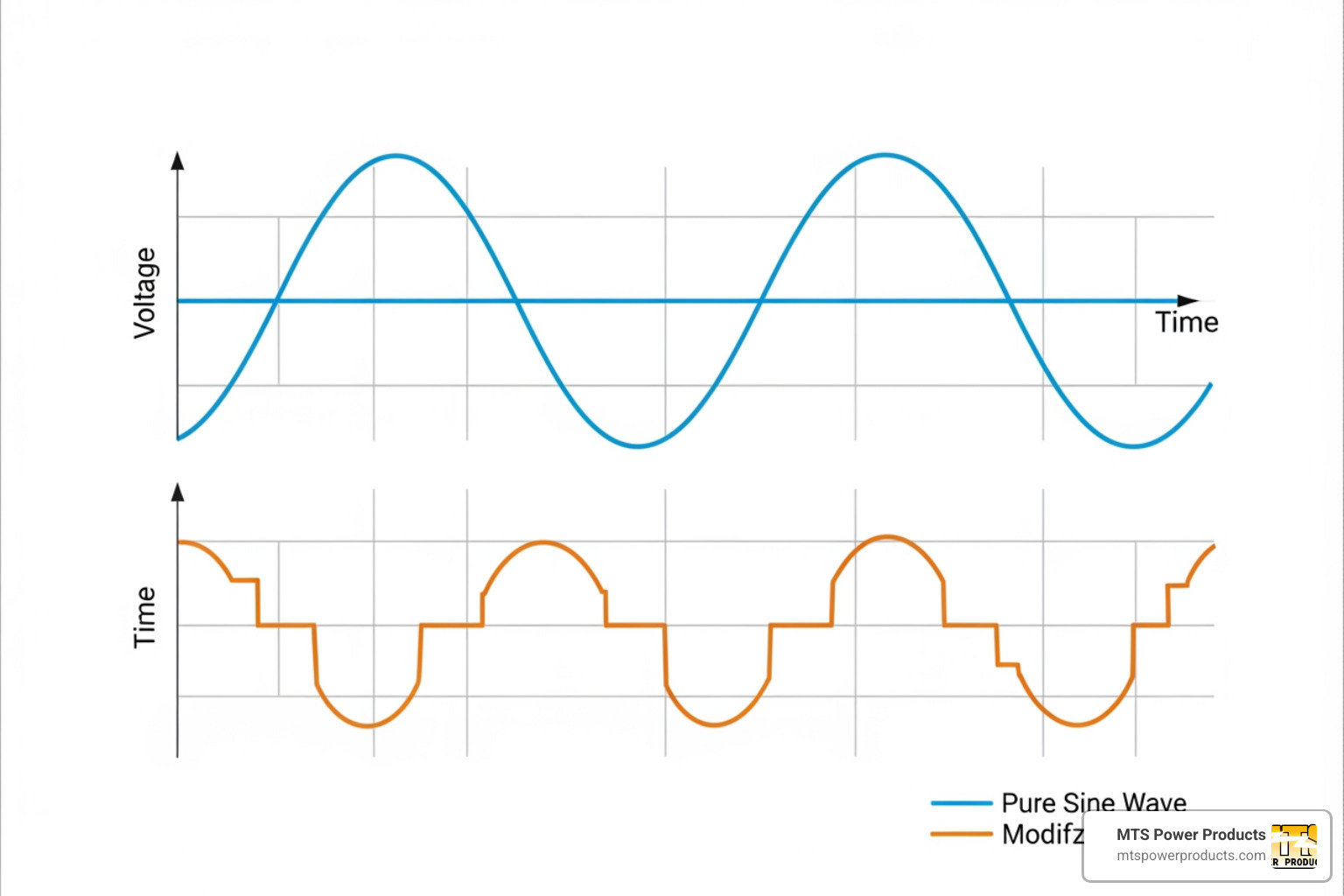
Conventional generators produce “dirty” power that can harm delicate circuits. Inverter generators produce stable, “clean” power with less than 3% THD, similar to what your wall outlets provide. If your backup plan includes running a home office or charging devices, an inverter generator for home use is a necessary investment. For smaller needs, portable power stations (large battery banks) offer a quiet, emission-free alternative for charging phones and laptops.
Owning a generator for home backup comes with serious responsibilities. Proper installation, strict safety adherence, and regular maintenance are essential to ensure your generator runs reliably and safely when you need it most.
The number one rule: Never, ever operate a fuel-based generator indoors. This includes garages, sheds, or carports, even with doors open. Generators produce carbon monoxide (CO), an odorless, colorless gas that can be lethal within minutes.
For more information, follow CPSC safe practices.
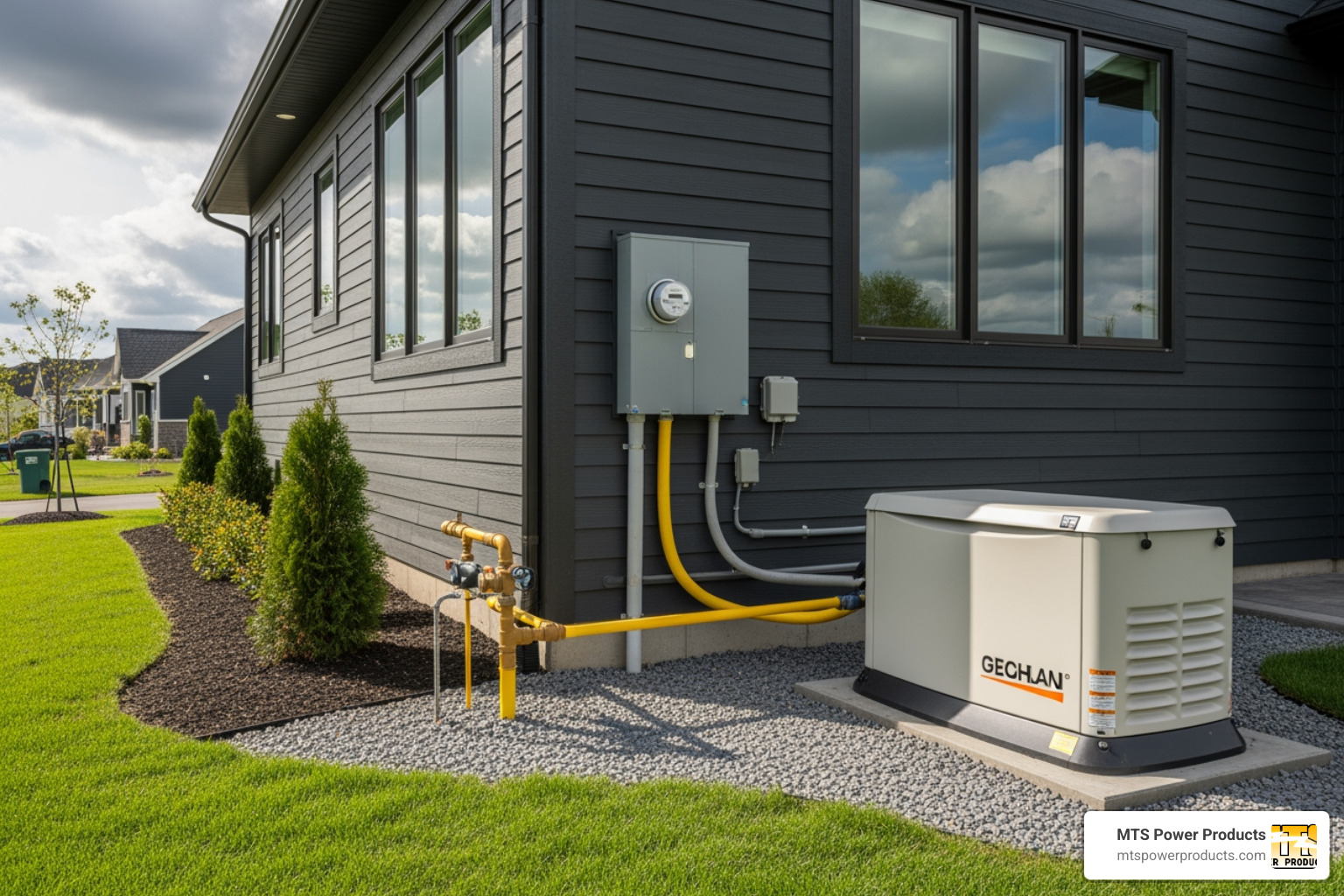

Understanding the full cost helps you choose the right generator for home backup.
Even if connecting a large portable generator to your breaker panel, you’ll need a professionally installed transfer switch for safe operation. For expert advice on solutions like a natural gas powered generator, consider working with a direct source manufacturer.
Like a car, your generator for home needs regular attention to perform reliably.
With good care, a portable generator can last 1,000 to 3,000 hours, translating to 10-30 years of typical use. Standby generators are built for even longer service. Warranties vary, but registering your product and keeping maintenance records is always a good practice to protect your investment.
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we get about generator for home use.
This depends on the fuel source and the electrical load.
This is a key distinction for powering modern electronics.
Yes, if you plan to connect a generator directly to your home’s electrical panel.
You now have the knowledge to select the right generator for home backup power. We’ve covered the differences between flexible portable units and automated standby systems, how to calculate your power needs, and why safety must always come first.
Whether you choose a budget-friendly portable or invest in a whole-home standby system, you’re making a smart choice for your family’s security. A generator keeps your essentials running—from refrigerators to medical devices—when the grid fails.
Proper installation and maintenance are key to reliability. Using a transfer switch and following a maintenance schedule ensures your generator is ready when you need it.
For professional advice on high-quality, custom solutions, consider a direct source manufacturer like MTS Power Products. Based in Miami, Florida, we specialize in custom generators and automatic transfer switches, including our own line of McPherson Controls. Our products feature advanced programmable displays and switch mechanisms for improved control and safety.
We are centrally located near the Miami International Airport and the Port of Miami, offering worldwide delivery. For homes with a utility line, a natural gas powered generator offers the most convenient and reliable backup power solution.
This investment is about more than equipment; it’s about peace of mind. Knowing your home stays powered and your family stays safe during an outage is the real value of a quality generator for home backup.