
Buy Direct
from the Manufacturer
Sell our Products
Become a Distributor
Discounts
on volume purchases
Visit Us
at our Miami office
from the Manufacturer
Become a Distributor
on volume purchases
at our Miami office
Improved safety features are technologies designed to prevent accidents and protect people from harm, ranging from automotive systems like Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) and lane-keeping assist to personal devices like Apple Watch crash detection. These features use sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to detect potential dangers and either warn users or take automatic action to prevent injury.
Key improved safety features you should know about:
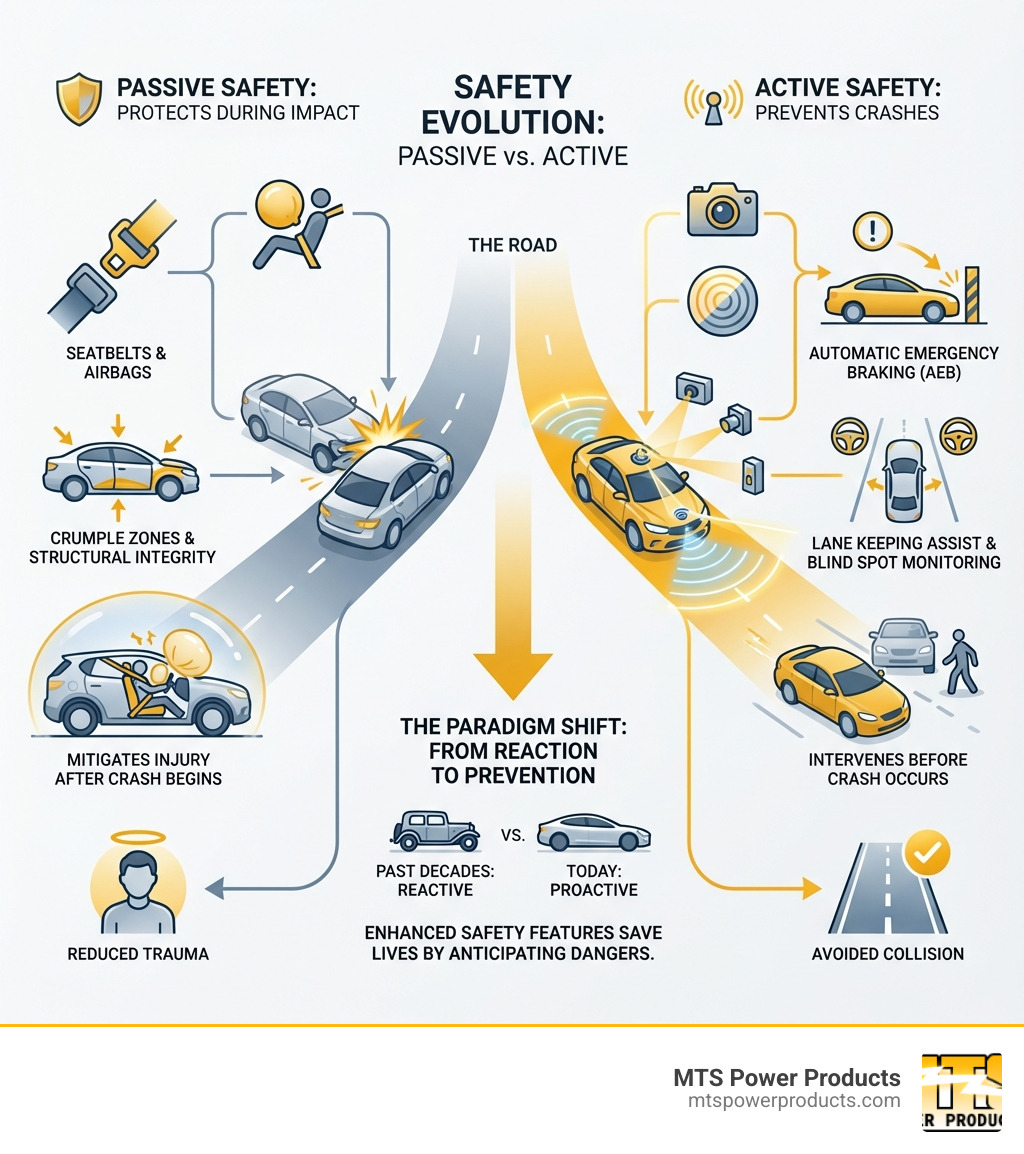
The past decade has brought a quiet revolution in safety technology. For decades, safety meant seat belts, airbags, and antilock brakes – features that protected you during a crash. Today’s systems are fundamentally different. They’re designed to prevent crashes from happening at all.
This shift from passive to active safety has saved hundreds of thousands of lives. According to NHTSA, improved safety technologies saved over 600,000 lives between 1960 and 2012. The average vehicle in 2012 had a 56% lower fatality risk compared to vehicles from the late 1950s.
But here’s the challenge: the average vehicle on American roads is 12.2 years old. That means millions of drivers are missing out on safety features that could save their lives.
Whether you’re shopping for a new vehicle, managing a facility that requires backup power systems, or simply trying to understand how modern safety technology works, this guide will help you steer the landscape of improved safety features and understand how they can protect you and your family.
Find more about improved safety features:
Looking back, it’s incredible to see how far vehicle safety has come. What started as basic protective measures has transformed into a sophisticated network of intelligent systems. Our journey through automotive history reveals a relentless pursuit of safety, driven by engineering advancements, in-depth research, and the crucial analysis of crash data. Newer vehicles are not just built better; they incorporate a multitude of improved safety features designed to protect us like never before.

The foundational safety features we now take for granted—like seat belts, airbags, and Electronic Stability Control (ESC)—have had an immeasurable impact on reducing fatalities. These innovations represent milestones in our collective effort to make roads safer. For a deeper look into this journey, the NHTSA provides an insightful overview of how vehicle safety has improved over the decades.
In the early days, safety primarily focused on passive measures—features that protected occupants during a crash. The humble seatbelt, for instance, evolved from simple lap belts to the now-standard three-point restraint systems with pretensioners that tighten instantly upon impact. Crumple zones, designed to absorb crash energy, also became a critical part of vehicle architecture. Airbags, once a novel concept, have been continuously reengineered to deploy safely and effectively for all occupants, expanding from frontal to side and side-curtain airbags.
However, the real game-changer has been the shift towards active safety—systems designed to prevent accidents from happening in the first place. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), first developed for aircraft in the 1920s and later adapted for cars, were pioneers in this field, preventing wheel lock-up during hard braking and allowing drivers to maintain steering control.
Mandatory safety features have played a pivotal role in this evolution. Electronic Stability Control (ESC), which uses computer-controlled braking to help drivers maintain control during skids, became a requirement in all new cars since September 1, 2011. More recently, rearview video systems (backup cameras) have been mandated in all new cars since May 1, 2018, significantly reducing backover accidents by providing a wider view and warning of approaching hazards.
The statistics paint a compelling picture of the success of these improved safety features. NHTSA estimates that vehicle safety developments have dramatically increased the annual number of lives saved, from a mere 115 in 1960 to a staggering 27,621 in 2012. Cumulatively, these improved safety technologies have saved over 600,000 lives between 1960 and 2012.
Let’s break down the impact of some key features:
These numbers underscore that investment in improved safety features isn’t just about convenience; it’s about life-saving innovation.
Today’s vehicles are veritable marvels of engineering, packed with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) that work tirelessly to keep us safe. These systems represent the latest advancements in vehicle safety features, acting as a co-pilot that’s always vigilant.
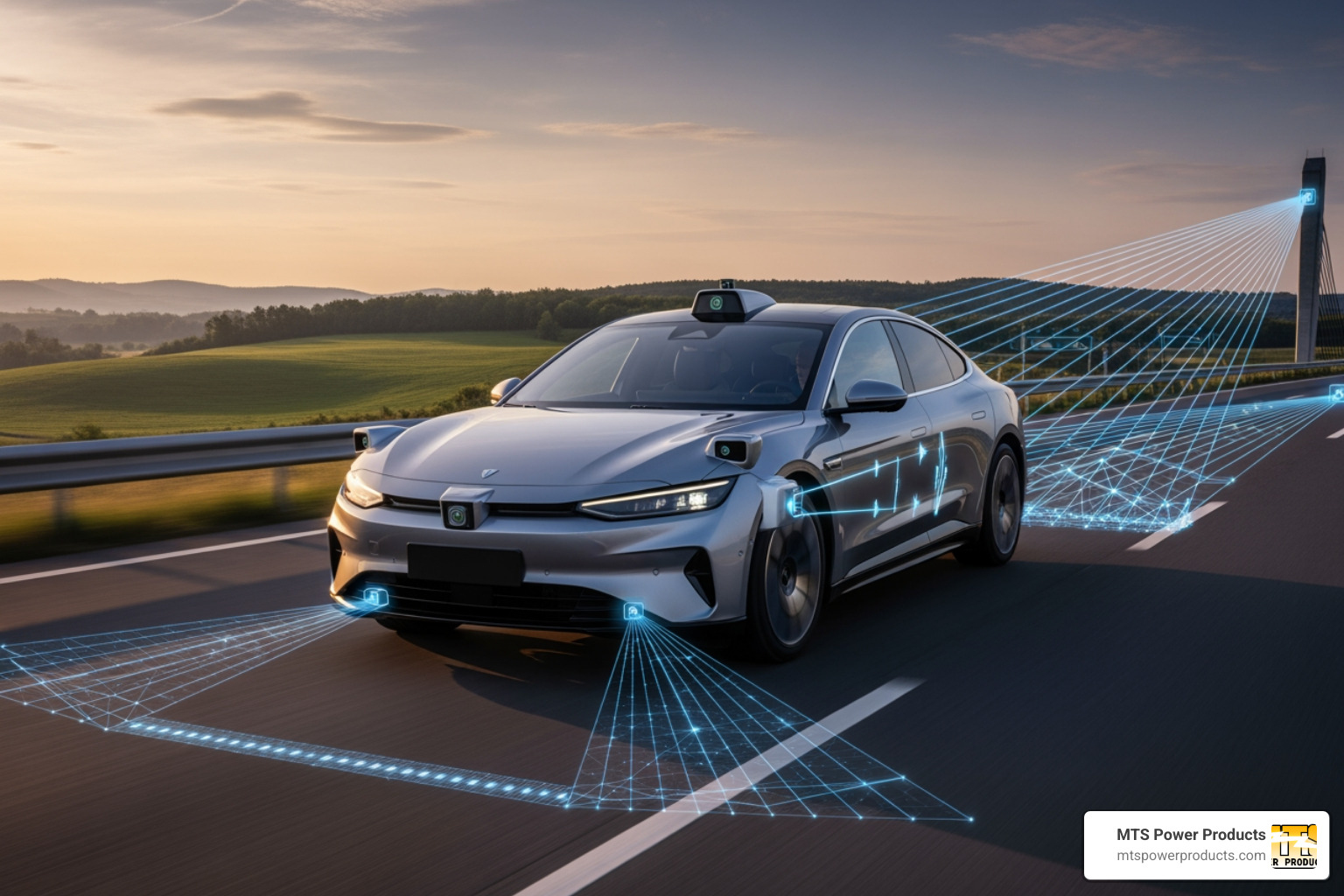

At the heart of these modern car safety systems is the intricate interplay of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and sophisticated sensors. Cameras, radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors continuously scan the environment around the vehicle, collecting vast amounts of data. AI algorithms then process this data in real-time, identifying potential hazards, predicting movements, and making instantaneous decisions. This is how new technologies like ADAS, AEBS, and lane keeping assist improve driver and passenger safety—by augmenting human perception and reaction capabilities. They don’t just warn; they interpret, predict, and often act faster than a human can. This integration of multiple active safety technologies into a single cohesive system, often referred to as a “Star Safety System™” by some manufacturers, is what makes modern vehicles so remarkably safe.
One of the most impactful categories of improved safety features is automatic crash avoidance. These systems actively work to prevent collisions, dramatically reducing the risk of accidents.
Beyond direct crash avoidance, many improved safety features focus on supporting the driver and increasing their awareness of the surrounding environment, preventing common errors that lead to accidents.
The advantages of vehicles equipped with these advanced safety systems extend far beyond just accident prevention. Investing in improved safety features offers a multitude of benefits for consumers:
Safety isn’t confined to the roads anymore. The principles of improved safety features are extending into our personal lives and shaping the future of how we interact with technology, ensuring protection in an ever-broader range of scenarios.
The Apple Watch, for example, has evolved significantly beyond a mere fitness tracker. With watchOS 26.2, Apple has introduced Improved Safety Alerts, marking a significant step in making wearables personal safety companions. This means the device is becoming more deeply embedded in our daily lives, acting as a guardian on our wrist. You can learn about Enhanced Safety Alerts and how they function.
How has the Apple Watch evolved to include improved safety alerts? Features like Fall Detection (debuted in Series 4) and Crash Detection (introduced in Series 8) automatically detect severe incidents and can initiate calls to emergency services if the user is unresponsive. Emergency SOS and Check In features further contribute to personal safety, allowing users to quickly summon help or share their location with loved ones.
The key difference between traditional emergency alerts and Apple’s Improved Safety Alerts lies in their context and clarity. Traditional alerts are often blunt, text-heavy, and lack specific details. Apple’s new alerts provide clearer descriptions of threats, location-aware context, and sometimes even visual elements like maps or guidance links. They are designed to be understood at speed, delivering critical information when it matters most. These alerts can be delivered directly to the Apple Watch over Wi-Fi or cellular, using live location, even without an iPhone nearby. This means that whether you’re on a hike or just out for a walk in Miami, your watch can provide timely safety information.
This evolution highlights a broader implication: automakers and tech companies are taking on a greater role in interpreting and delivering safety data. They are increasingly becoming curators of critical information, deciding how, when, and in what form safety information reaches us.
The future of automotive safety promises even more groundbreaking advancements, moving towards a highly connected and autonomous driving experience.
In our pursuit of safety, it’s not enough to simply have advanced features; we also need robust standards and reliable ways to evaluate them. This is where government agencies and independent organizations play a crucial role, acting as watchdogs and guides for consumers.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) are two such pillars in vehicle safety. NHTSA, a U.S. federal agency, sets and enforces safety standards, while IIHS is an independent, non-profit scientific and educational organization dedicated to reducing deaths, injuries, and property damage from motor vehicle crashes. Together, they push manufacturers to innovate and provide consumers with transparent safety information.
For consumers, navigating the myriad of safety claims can be daunting. This is where safety ratings become invaluable.
These ratings help consumers choose safer vehicles by providing an objective, standardized assessment of a vehicle’s protective capabilities. They also drive manufacturer improvements; when IIHS introduced the small overlap test, for instance, many automakers redesigned their vehicles to achieve better scores, demonstrating how ratings push the industry forward.
Beyond ratings, government mandates are essential in ensuring that critical improved safety features become standard for everyone, not just those who can afford premium packages.
| Feature Type | NHTSA Role | IIHS Role | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crashworthiness | Sets FMVSS for structural integrity, conducts 5-star crash tests | Conducts independent crash tests (e.g., small overlap, side), awards Top Safety Pick | Protects occupants during a crash, drives structural improvements |
| Crash Avoidance | Mandates features like rearview cameras, sets standards for AEB | Evaluates effectiveness of ADAS features, awards points for superior/advanced ratings | Prevents crashes, reduces severity, saves lives |
Backup cameras, for example, have been a required safety technology on all new cars since May 1, 2018, significantly reducing backover accidents. More recently, NHTSA finalized a rule making Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) standard in all new cars and light trucks starting in 2029. This mandate, fulfilling a provision in the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, requires all cars to stop and avoid contact with a vehicle in front up to 62 mph and detect pedestrians up to 45 mph. This rule alone is estimated to save at least 362 lives and mitigate 24,321 non-fatal injuries a year. The significance of mandatory safety features like AEB and backup cameras in new vehicles is clear: they standardize safety, ensuring a baseline level of protection for all road users.
Our journey through improved safety features reveals a profound evolution—from passive protection during a crash to proactive systems designed to prevent accidents altogether. This change, powered by the relentless advancement of sensors, AI, and integrated technologies, has demonstrably saved hundreds of thousands of lives and continues to redefine what it means to be safe on the road.
The principles behind these sophisticated systems—constant monitoring, intelligent analysis, and automated response—are not limited to passenger vehicles. They are increasingly relevant across a broad spectrum of applications, including industrial equipment and power generation systems. Just as a vehicle’s ADAS prevents collisions, advanced safety controls in industrial machinery can prevent operational hazards and protect personnel.
At MTS Power Products, we understand that safety is paramount, whether it’s on the highway or in a critical power installation. As a manufacturer and provider of generator sets, control panels, voltage regulators, and more, we apply these same high safety standards to our products. Our customized line of professional quality commercial & residential power controls, McPherson Controls, integrates programmable displays and switch mechanisms for improved control and safety. We offer the distinct advantage of being a direct source for professional quality products with advanced features like remote monitoring and high safety standards.
We are proud to serve the Miami, Florida area, and beyond, providing custom generators, transfer switches, and other electrical products that prioritize safety and reliability. Our commitment to incorporating robust safety features ensures that our solutions not only power your operations but also protect your assets and personnel.
To learn more about how we integrate advanced safety into our power solutions, we invite you to explore commercial backup generators with advanced safety controls. Let us help you accept a safer future, powered by cutting-edge technology.
